SKAT, SKAT-O 가 어떤 수식으로 계산되는지와 weight를 어떻게 주어야 하는지, small-sample 에서는 어떻게 adjust해서 type I error 를 줄였는지 자세히 적혀있다.
Seunggeun Lee, Mary J Emond, Michael J Bamshad, Kathleen C Barnes, Mark J Rieder, Deborah A Nickerson, NHLBI GO Exome Sequencing Project—ESP Lung Project Team; David C Christiani, Mark M Wurfel, Xihong Lin
AJHG VOLUME 91, ISSUE 2, P224-237, AUGUST 10, 2012
Published:August 02, 2012
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.06.007
Highlight
.. a unified approach for testing the association between rare variants and phenotypes in sequencing association studies. This approach maximizes power by adaptively using the data to optimally combine the burden test and the nonburden sequence kernel association test (SKAT).
.. to develop a small-sample adjustment proocedure for the proposed methods for the correction of conservative type I error rates of SKAT family tests ..
Rare variants might play an important role in the etiology of complex traits and account for missing heritability unexplained by common variants.
Single-variant tests are typically conducted to investigate associations of common variants and phenotypes; however the same approach has little power for testing for rare-variant effects because of their low frequencies and large numbers.
Burdne tests collapse rare variants in a genetic region into a single burden variable and then regress the phenotype on the burden variable to test for the cumulative effects of rare variants in the region.
.. SKAT aggregates individual variant-score test statistics with weights when SNP effects are modeled linearly. More generally, SKAT aggregates the associations between variants and the phenotype through a kernel matrix and can allow for SNP-SNP interactions, i.e., epistatic effects.
SKAT is derived as a variance-component test in the induced mixed models wherein regression coefficients are assumed to be independent and follow a distribution with the variance component.
.. to improve the performance of SKAT and SKAT-O in small-sample case-control sequencing association studies.
This allows us to precisely calculate the reference distribution for a small sample, thereby properly controlling the type I error.
Sequence Kernel Association Test
Several approaches have been proposed to reduce the df and increase analysis power.
Two classes of tests have been proposed: burden and nonburden tests.
The burden score statistic for testing H0: βc=0 is

The SKAT statistic is

.. the burden test aggregates the variants first before performing regression, whereas SKAT aggregates individual variant-test statistics. Hence, SKAT is robust to the mixed signs of βs and a large fraction of noncausal variants.
Optimal unified association test
.. derived as the variance component score statistic assuming the regression coefficients βj in Equation 1 follow an arbitrary distribution with mean 0 and variance wj^2τ ..
In practice, the optimal weight ρ is unkown and needs to be estimated from the data to maximize the power.

.. one asymprotically follows a chi-square distribution with one df, and the other can be asymptotically approximated to a mixture of chi-square distributions with a proper adjustment.
Small-sample optimal unified test
.. have beedn found to produce conservative results, which can lead to incorrect type I error contral and power loss.
.. small-sample-adjusted p value calculations ..
When variants are rare, and the genotype matrix G is sparse, the small-sample variance of Qs is much smaller than the asymptotic variance. Hence, we readjust the moments of the null distribution of Qs.
.. U=[i1,...,uq] be an nxq eigenvector matrix of K ..

.. the small-sample mean of Qs is the same as the asymptotic mean of Qs, but the small-sample variance differs from the asymptotic variance.
With the use of the estimated moments, the p-value can then be calculated as

where F(·|χ2) is the distribution function of χ2, and
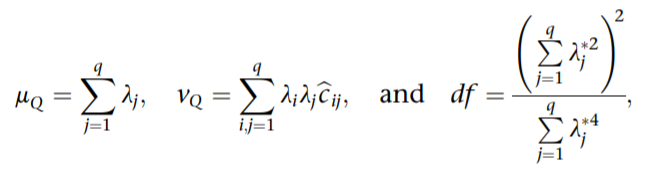
Small-sample SKAT and unified test with higher moments adjustments
When there is no covariate, the kurtosis of the null distribution of Qs can be estimated from B permutation samples of phenotypes, and them the estimated kurtosis can be used to calculate the df parameter in Equation 11.
We first estimate πi under the null model and use it to generate Yb with same number of cases and controls.
For whole-exome sequencing studies, one needs to calculate p values at the 10^-5~10^-6 level to account for multiple comparison adjustments for performing tests for 20,000 genes. This requires more than 10^7~10^8 permutations or bootstraps for each gene. However, our approach requires sampling phenotypes under the null model only 10,000 times to obtain stable estimates of the higher moments.
Result
Note that α=2.5x10^-6 is Bonferroni-adjusted level α=0.05 when simultaneously testing 20,000 genes.
Overall, out type I error simulation results confirm empirically that the proposed small-sample adjustment methods accurately control type I error rates.
.. all causal variants were deleterious variants, i.e., that the effects of the causal variants were all in the same direction.
.. assumptions to those of the burden tests; i.e., it requires a majority of rare variants under the optimal threshold to be causal and have effects in the same direction. The EREC method requires estimation of regression coefficients, which are difficult to estimate stably for rare variants.
.. SKAT-O and its small-sample adjustment compute p values efficiently and can be easily applied to whole-exome and whole-genome sequencing studies.


댓글